By Sarah Jenkins
Published: October 26, 2025
Location: Detroit, Michigan
Revitalizing the Motor City: How Modernization is Reshaping Detroit Factories
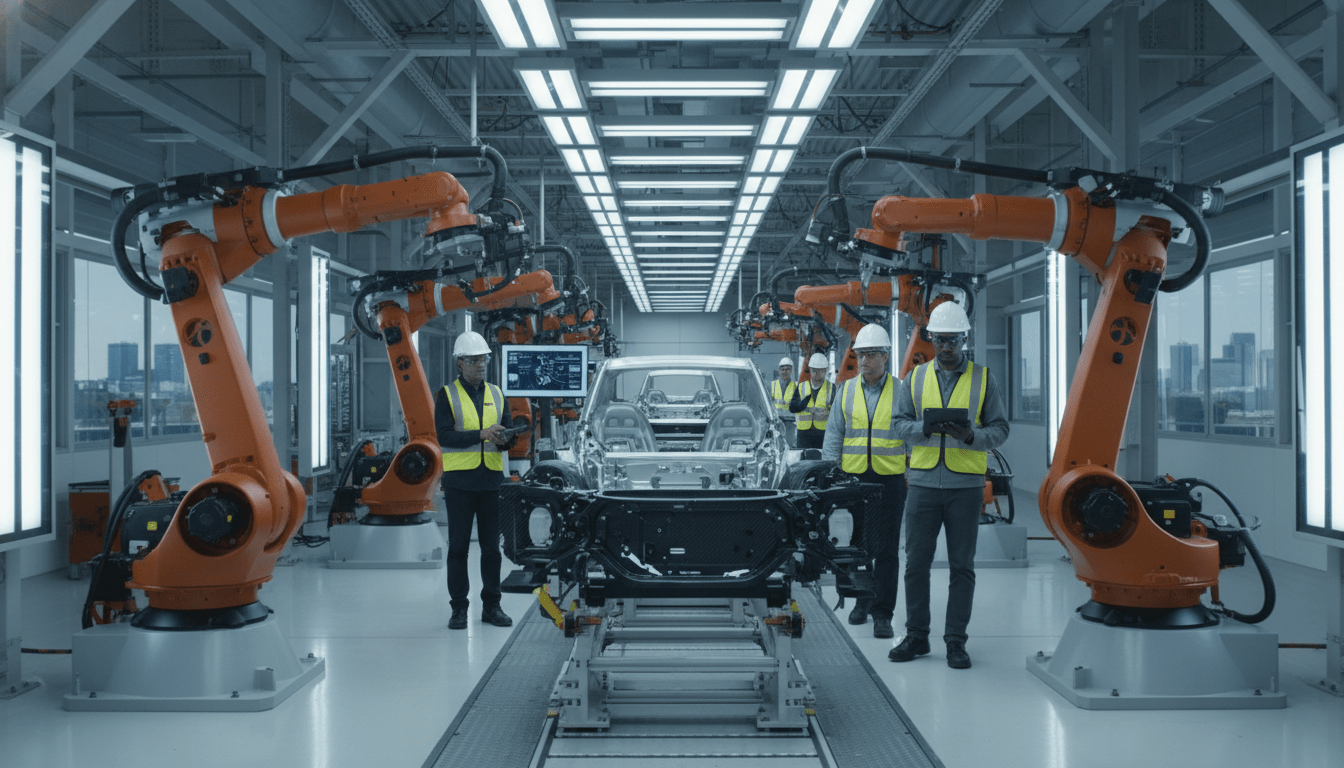
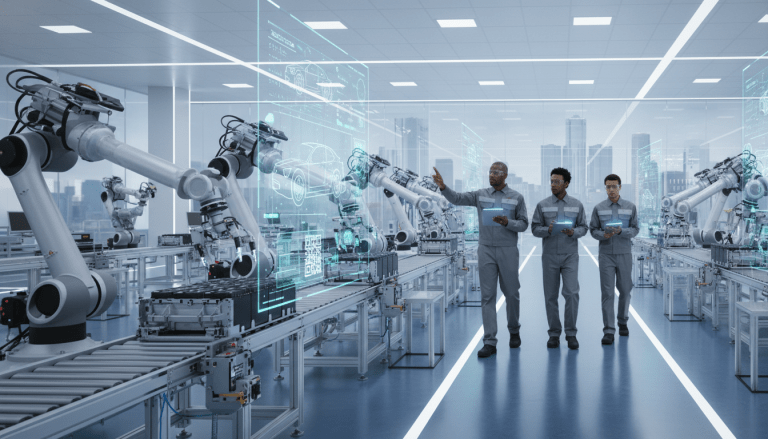
For decades, the image of Detroit manufacturing was defined by grit, steam, and manual assembly lines. Today, that image is rapidly being replaced by clean rooms, collaborative robotics, and artificial intelligence. Detroit manufacturing modernization is not just a buzzword; it is a fundamental economic shift that is redefining the city’s industrial landscape and the skills required to work within it.
As the automotive industry pivots aggressively toward electric vehicles (EVs) and sustainable practices, Detroit’s legacy plants are undergoing multi-billion dollar overhauls. From General Motors’ Factory ZERO to smaller Tier 1 suppliers in the metro area, the transition to Industry 4.0 is securing Detroit’s place in the global economy while presenting new challenges and opportunities for the local workforce.
The Shift to Smart Manufacturing
The core of this transformation lies in the integration of digital technology into physical production. According to reports from the Michigan Economic Development Corporation (MEDC), the state has seen a significant uptick in capital investment directed specifically toward automation and digitization.
Major automakers are leading the charge. General Motors, for instance, has successfully repurposed the Detroit-Hamtramck Assembly Center into Factory ZERO, a facility dedicated entirely to EV production. This required stripping the plant down to its studs and rebuilding it with flexible tooling and autonomous mobile robots. Similarly, Stellantis has invested heavily in updating its Jefferson North assembly plant to handle modern vehicle architectures.
“The factory floor of 2025 looks nothing like the floor of 1995,” noted a representative from the Michigan Manufacturers Association in a recent industry brief. “We are seeing a convergence of IT and operations technology where data is just as valuable as the steel being stamped.”
Impact on Detroit Residents
For the people of Detroit, this modernization brings a mixed bag of immediate disruption and long-term opportunity. The most significant change is the nature of the jobs available.
Traditional manual labor roles are declining, but they are being replaced by high-tech positions that often pay higher wages. Residents looking to enter the manufacturing sector now need skills in robotics maintenance, systems monitoring, and data interpretation.
To address this skills gap, local initiatives are ramping up. The City of Detroit’s workforce development programs have increasingly focused on upskilling workers for the digital age. Local technical colleges are partnering with factories to create curriculums that match the specific needs of modern assembly lines.
“It is no longer about just standing on a line; it is about managing the machines that run the line,” said a program director at a local vocational training center. “This shift allows workers to save their bodies from wear and tear while engaging their minds, but it requires a commitment to continuous learning.”
Background & Data: The Economic Ripple Effect
The push for Detroit manufacturing modernization is driven by efficiency and sustainability. Data from the National Association of Manufacturers indicates that for every $1.00 spent in manufacturing, another $2.60 is added to the economy. In high-tech manufacturing, that multiplier is often even higher due to the complex supply chains involved.
Furthermore, modernization is critical for environmental compliance. New factories are designed to be carbon-neutral, using energy-efficient lighting, recycled water systems, and renewable energy sources. This directly benefits Detroit neighborhoods surrounding industrial zones, which have historically suffered from higher pollution levels.
For more on how local businesses are adapting, read our coverage on Detroit small business grants helping suppliers upgrade.
What Happens Next
The trajectory for Detroit is clear: the integration of AI and machine learning will only deepen. Experts predict that within the next five years, “predictive maintenance”—where machines alert humans to repairs before they break—will be standard in 90% of Detroit’s major factories.
As the city continues to attract tech startups focusing on industrial IoT (Internet of Things), the line between “Silicon Valley” and “Motor City” continues to blur. For Detroiters, staying ahead of this curve is essential. The factories are staying, but they are evolving, and the workforce must evolve with them.
Read more about the city’s economic outlook in our report on Detroit’s 2026 Economic Forecast.